Which Of The Following Registers Is Used To Pass Parameters To Functions (Callees)?
6.3. Part Arguments and Parameters
People, even experienced programmers, often use the terms "argument" and "parameter" interchangeably and rely on context to clarify the verbal significant (if an exact meaning is fifty-fifty needed). This exercise generally doesn't cause whatsoever misunderstanding because whichever term is used, the basic idea is that data is passed from a function phone call into a function for processing. Nevertheless, parameters are local variables defined in the office (inside of parentheses in the function header) and used to hold the data passed into the function. Arguments are the values passed from a function call (i.e., they are the values appearing inside the parentheses of the call) and are sent into the part).
The following example is based on pass-past-value, the most common and familiar argument passing technique. However, C++ as well supports (what we will phone call) pass-by-pointer and pass-by-reference. The deviation in the behaviors of the 3 argument-passing techniques is the subject of the subsequent sections.
| Arguments | Parameters | Event |
|---|---|---|
| Actual parameters | Formal parameters | |
| Appear in function calls | Announced in function definitions | |
sqrt(ten); | double sqrt(double y) { ... } | y = x; |
double y = sin(M_PI /4); | double sin(double angle) { ... } | angle = M_PI/four; |
payment = payment(100000.00, 0.08, 30); | double payment(double p, double r, int north) { ... } | p = 100000.00; r = 0.08; n = 30; |
Argument and Parameter Names
When a function'southward arguments are variables, the argument names (in the function call) and the parameter names (in the part definition) may exist the same or they may exist different.
| Same | Different | |
|---|---|---|
| Telephone call (Arguments) | function(10); | function(y); |
| Definition (Parameters) | void part(int 10) { . . . } | void part(int z) { . . . } |
When a program passes data into a function, it matches the arguments (in the phone call) to the parameters (in the office) based on position. And then, each argument must correspond to exactly 1 parameter based on position. The programme determines position by counting the comma-separated elements from left to right. All three argument-passing techniques share this positional matching.
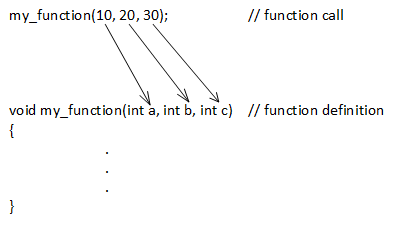
Which Of The Following Registers Is Used To Pass Parameters To Functions (Callees)?,
Source: https://icarus.cs.weber.edu/~dab/cs1410/textbook/6.Functions/args.html
Posted by: wheelersuchancessim1968.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Which Of The Following Registers Is Used To Pass Parameters To Functions (Callees)?"
Post a Comment